Heidi Worley
Former Program Director

Road traffic accidents—the leading cause of death by injury and the tenth-leading cause of all deaths globally—now make up a surprisingly significant portion of the worldwide burden of ill-health. An estimated 1.2 million people are killed in road crashes each year, and as many as 50 million are injured, occupying 30 percent to 70 percent of orthopedic beds in developing countries hospitals.1 And if present trends continue, road traffic injuries are predicted to be the third-leading contributor to the global burden of disease and injury by 2020.2
Developing countries bear a large share of the burden, accounting for 85 percent of annual deaths and 90 percent of the disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) lost because of road traffic injury.3 And since road traffic injuries affect mainly males (73 percent of deaths) and those between 15 and 44 years old, this burden is creating enormous economic hardship due to the loss of family breadwinners (see Figure 1).
Figure 1
Road Traffic Deaths Worldwide by Sex and Age Group, 2002
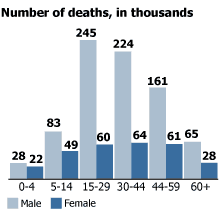
Source: WHO Global Burden of Disease Project, Version 1 (2002).
Road traffic injuries are predictable and preventable, but good data are important to understand the ways in which road safety interventions and technology can be successfully transferred from developed countries where they have proven effective. Awareness of the consequences of road traffic injuries is lagging among policymakers and the general public. What’s needed is incorporation of comprehensive road safety programs into national planning in developing countries.
In developed countries, road traffic death rates have decreased since the 1960s because of successful interventions such as seat belt safety laws, enforcement of speed limits, warnings about the dangers of mixing alcohol consumption with driving, and safer design and use of roads and vehicles. For example, road traffic fatalities declined by 27 percent in the United States and by 63 percent in Canada from 1975 to 1988. But traffic fatalities increased in developing countries during the same period—by 44 percent in Malaysia and 243 percent in China, for instance.4
More than one-half of all road traffic deaths globally occur among people ages 15 to 44—their most productive earning years. Moreover, the disability burden for this age group accounts for 60 percent of all DALYs lost because of road traffic accidents.5 The costs and consequences of these losses are significant. Three-quarters of all poor families who lost a member to road traffic death reported a decrease in their standard of living, and 61 percent reported they had to borrow money to cover expenses following their loss.6 The World Bank estimates that road traffic injuries cost 1 percent to 2 percent of the gross national product (GNP) of developing countries, or twice the total amount of development aid received worldwide by developing countries.7
As in developed countries, driver impairment is an important component of road traffic accidents in developing countries. Driving at excess speeds, while under the influence of alcohol or drugs, while sleepy or tired, when visibility is compromised, or without protective gear for all vehicle occupants are major factors in crashes, deaths, and serious injuries.
In general, pedestrians, cyclists, and moped and motorcycle riders are the most vulnerable road users as well as the heaviest users of roads in poor countries. Most people who use public transportation, bicycles, or mopeds and motorcycles or who habitually walk are poor, illuminating the higher risk borne by those from less privilege.8 In Asia, for instance, motorized two- and three-wheelers (such as motorized rickshaws) will make up the anticipated growth in numbers of motor vehicles.9 Figure 2 shows the higher proportion of deaths among these groups in developing countries.10
Figure 2
Proportion of Road Users Killed in Various Modes of Transport As A Percent of All Fatalities, Selected Countries
|
Country
|
Pedestrians
|
Bicyclists
|
Motorized vehicles
|
Others
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Two-wheeled
|
Four-wheeled
|
||||
| Thailand |
47
|
6
|
36
|
12
|
—
|
| Malaysia |
15
|
6
|
57
|
19
|
3
|
| United States |
13
|
2
|
5
|
79
|
1
|
*Note: Dates for above data vary according to city and country: Thailand, 1987; Malaysia, 1994; and United States, 1995.
Source: Dinish Mohan, “Traffic Safety and Health in Indian Cities,” in Journal of Transport and Infrastructure no. 9 (2002).
The World Bank and the World Health Organization (WHO) advocate a “systems approach” to road traffic safety that emphasizes involvement at all levels of the road traffic system—from road providers and enforcers (vehicle manufacturers, road traffic planners, road safety engineers, police, educators, health professionals, and insurers) to road users. Prevention interventions fall into several broad categories:
Managing risk exposure with land-use. In developing countries, exposure to potential road traffic injury has increased largely because of rapid motorization, coupled with poor road conditions, rapid population growth, lack of safety features in cars, crowded roads, poor road maintenance, and lack of police enforcement. For example, in Vietnam, the number of motorcycles grew by 29 percent in 2001, with an associated increase of 37 percent in the number of road traffic deaths.11
Promoting efficient patterns of land use and providing shorter, safer routes for vulnerable road users can reduce their exposure. Studies in Brazil, Mexico, and Uganda have found that pedestrians would rather cross a dangerous road than go out of their way to take a pedestrian bridge, even though such preferences increased their exposure to injury risk.12
Improving public transportation systems can also reduce exposure. People in cars are between 8 and 20 times less likely to be killed in a road accident than walkers, bicyclists, or motorized two-wheeler users.13
Planning and designing roads for safety. In almost all countries, road networks are designed from the perspective of the motor vehicle user. But developing countries can take lessons from safety conscious road design in countries such as the Netherlands and Denmark, where roads are built to suit their function (high speed, rural, transitional between high speed and rural, and residential) and account for the safety of pedestrians and cyclists. Studies in Denmark showed that providing segregated bicycle lanes alongside urban roads reduced deaths among cyclists by 35 percent.14
Providing visible, crashworthy, and smart vehicles. Designing motorized vehicles that are more crashworthy is an important intervention in those developing countries where automobile safety regulations are more lax than in developed countries. One study showed that in developing countries, buses and trucks are involved in a much greater proportion of crashes, yet lack relevant safety standards.15
Improving vehicular visibility is also important. In Thailand, hospital records showed that 75 percent to 80 percent of road traffic injuries were among users of motorized two-wheeled vehicles, which are not easily visible to larger vehicle operators. Improving the visibility of drivers in other instances (such as at night or during fog) can reduce injuries. Daytime running lights and high-mounted stop lamps have improved crashes in these cases, as have reflectors and colorful clothing.
New technologies have created other avenues for road safety. These developments include intelligent speed adaptation, in which the vehicle determines the speed limit for the road; alcohol-ignition interlock systems that detect alcohol on the breath of drivers, preventing them from starting their engines; or electronic driver improvement monitors that connect individual driver profile assessments and an individual vehicle operator’s actual driving performance.
Setting road and safety rules, securing compliance, and improving transport policy. Setting and enforcing speed and blood alcohol concentration limits have proven to be perhaps the most successful interventions contributing to the decrease in injury in developed countries. Speed limiting devices on vehicles, limits on engine power, and nonvehicular traffic-calming measures hold the greatest promise in developing countries, according to Dinesh Mohan, professor of biomechanics and transportation safety coordinator with the Transportation Research and Injury Prevention Programme at the Institute of Technology in New Dehli, India.16
Enforcing blood alcohol limits is another opportunity to improve road safety. While it is commonly understood in developed countries that impaired driving is an important contributor to road traffic fatalities and injuries, little is known in these countries about the nature and scope of the problem. One survey of studies found that, in developing countries, blood alcohol was present in 33 percent to 69 percent of fatally injured drivers.17
Because blood alcohol tolerances vary across countries, comparison studies are difficult, and to date, no study has provided the evidence to benchmark the tolerance level at which reductions in accidents can occur in developing countries. David Bishai, an injury prevention expert and associate professor at Johns Hopkins University ‘s Department of Population and Family Health Sciences, suggests that taxing gasoline and alcohol could lower traffic deaths by causing less driving and less drunk driving in developing countries. But he warns that other measures must be taken and must fit the needs of the local environment.
Finally, although mandatory seat-belt-use laws have reduced traffic injuries in developed countries by 40 percent to 50 percent, such laws must be tailored to the local situation: In developing countries, car occupants constitute less than 10 percent to 20 percent of traffic fatalities.18 These countries also need to improve helmet safety and use among two- and three-wheel vehicle operators as well as to enforce the appropriate number of passengers for these vehicles.
Although some interventions from developed countries (such as the road-safety design elements in Denmark and the Netherlands) can be applied in developing-country settings, analysts urge caution because interventions are often situation-specific. Interventions need to be applicable to the particular mix of developing country road use—which is dominated by two-wheel vehicles, human-powered vehicles, pedestrians carrying loads, and locally designed vehicles. In addition, the traffic patterns in developing countries (especially in urban areas) are more complex because of high-density living and mixed land use, severe limitation of resources, and the abundance of shantytowns.19
